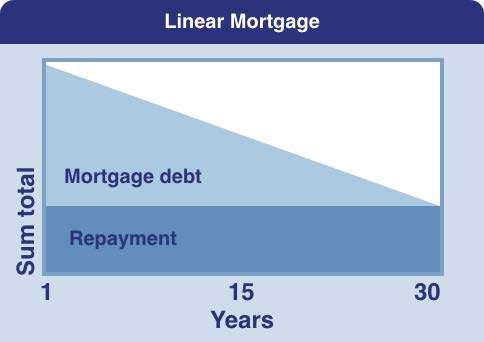
Annuity mortgage
The gross monthly charge (the amount you have to pay the financial institution) remains the same throughout the term. However, the composition of this constant monthly amount changes. During the term, the interest portion of this constant amount declines, and the repayment portion increases. Since only the interest is tax-deductible, with this form of mortgage the net charges increase as the loan gets older.
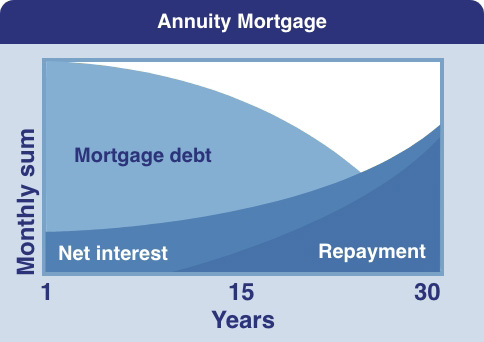
Linear mortgage
The linear mortgage is the most simple form of mortgage to understand. The main reason is that you repay the initial loan by a fixed amount every month. On top of this, you pay interest, but the interest payments will reduce over time since you are gradually redeeming the initial loan. Since the mortgage amount will actually decrease, so will your interest payments. A linear mortgage can be useful for people who wish to repay their mortgage as quickly as possible. However, the initial monthly repayments are relatively high. With a linear mortgage, you are repaying quicker than with an annuity mortgage. This means that during the term of the mortgage you pay less interest and that makes the mortgage cheaper in the end.
Mortgage for those who already have (had) a property
If you already own a property, and you are planning to buy a new home where you will also be living yourself, then the help of a mortgage adviser is a must. The reason is that there are many aspects to consider that are important for excellent advice. It would go too far to discuss these aspects in detail here, but we will highlight a few.
- If you bought a house before January 1st, 2013, there is transitional law, and you may be able to take your existing mortgage form with you. This can be interesting for example for interest-only mortgages.
- A good check of your old mortgage condition is also important. If the interest rate on your current contract is higher than the market interest rate of the new mortgage, you want to know if you can get rid of your old mortgage without penalties. On the other hand, if the interest rate for a new mortgage is higher, then it may be interesting to move the old mortgage with you to the new home to be purchased. In that case, you will want to know carefully what conditions the mortgage lender will impose for such a construction. There is always a time limit on moving your interest rate contract with you to the new home.
As mentioned, it is an important matter, but know that we are happy to assist you! Below, you will find several “old” mortgage types that you – as an existing homeowner – may be able to take with you to your new home.
Interest-only mortgage
With an interest-only mortgage, you pay only interest and the loan does not have to be repaid until the property is sold or the borrower dies.
The advantage of this is the low monthly charge. The disadvantage is that you are not doing any (tax-friendly) capital formation, so it is uncertain whether, at the end of 30 years, you will be able to repay the loan from the available funds. Repayment in some form is recommended, since the mortgage interest is deductible for up to 30 years.
(Bank) endowment mortgage
With a (bank) endowment mortgage, you make no repayments during the term of the mortgage, so with this form of mortgage, the interest deduction is the maximum throughout the entire term.
The most important characteristic is the guaranteed interest growth in the endowment policy. Interest equal to the mortgage interest rate is paid on the monthly premium that is payable. Besides a constant gross and net charge during the term (provided the interest rate does not change), another important advantage is that at the end of the term, the entire debt is guaranteed to be repaid.